What Does the IRS Extending the R&D Tax Credit Claims Transition Period Mean?
Qualification: The 4-Part Test
Permitted Purpose
The activity must be intended to develop or improve a business component’s (product, manufacturing process or software):
- Functionality
- Performance
- Reliability
- Quality
Elimination of Uncertainty
The activity must be intended to discover information to eliminate technical uncertainty concerning the capability or method for developing or improving a product or process, or the appropriateness of business component design.
Technological in Nature
Source Advisors reclassified 9% or $2,013,000 into Qualified Leasehold Improvement Property 3% or $605,000 to 15-year land improvements and 20% or $4,421,000 as 7 and 5-year tangible personal property. In this example, the taxpayer had chosen to opt-out of bonus depreciation in most years, if the full benefits of bonus depreciation were realized, the benefits would have been higher.
Process of Experimentation
Substantially all of the activities must be elements of a process of experimentation:
- Developing one or more hypotheses (design alternatives or prototyping)
- Designing and conducting experiments to test and analyze those hypotheses
- Refining or discarding those hypotheses to design the business component
- Modeling, simulation, trial and error testing
Qualified Research Expenses Include:
- Wages including direct support & direct supervision
- Supplies
- Contract Research Expenses
- Must retain rights & risks to the research performed
- Limited to 65% of total costs
- Computer Rental and Cloud
The next question we often get is: “How do we accumulate the expenditures for the R&D tax credit?”
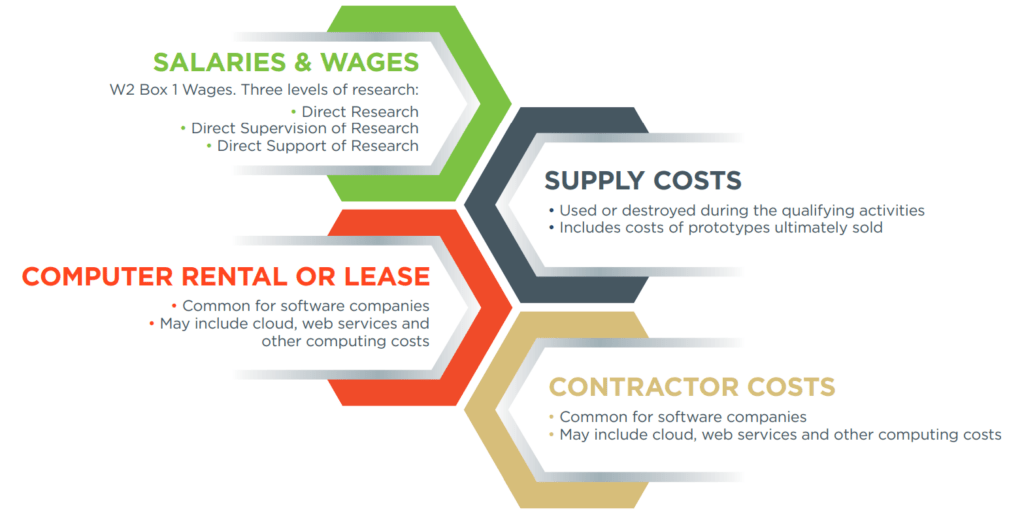
1. Salaries & Wages
Your expenditures for R&D include internal costs such as salaries, wages, supplies, computer rental, lease, etc. and external expenditures such as your contractor costs. There are three components of salaries and wages:
- Direct research. This includes people specifically performing the activities, (researchers, engineers, CAD associates, project managers, etc.) and is the core of the credit.
- Supervisors. Anyone who is directly supervising employees doing the direct development.
- Direct support of research. Let’s say a researcher has a direct assistant who is strictly taking notes and
accumulating data. Their time assisting the direct researcher is also included.
2. Supply Costs
If you are doing prototyping and testing of materials, the cost of those materials can be included as well. When you look at the construction and A&E industries, we’ve seen applicability for things like a new formulation of concrete or other building materials.
3. Computer Rental or Lease
This one is not seen as often, although it’s becoming more prevalent with software development needed to run complicated research algorithms and testing techniques. You can take the cost to lease a powerful computer for research activities. We’re also seeing it on the cloud storage space that’s specifically dedicated to research activities.
4. Contract Research
Often you can include contractors/outside resources that you hire as long as those resources are directly associated with your research activities. For instance, if you need to hire a specialist with electrical engineering expertise, you can include 65% of those expenditures for research activities for outside researchers.
A typical construction project has several stages. At each stage there are levels of qualification, typically toward the front end of the process in which you’re doing your estimating, bidding, design, development, and documentation. Once you get into the construction and completion phases, you start to see the phaseout of R&D qualifying activities. That’s because your uncertainties have been mostly phased out, if not entirely. Again, we want to focus on uncertainty. When you start a project, you have uncertainties. Over time you work through them. Once you are certain to a high degree that your proposed method is going to work, then you are through your R&D process.
General Construction
- Development of estimates based on designs provided by architects or engineers
- LEED and green initiatives
- Evaluation of engineering and construction methods for improvement in build time or overall performance and reliability
- Development of prefabrication processes
- Development of unique material transfer systems on project sites (e.g. crane design)
- Development of temporary support structures for active construction
- Testing and validation of new mechanical systems to solve technical uncertainties
- Building Information Modeling (SIM), AutoCAD and Revit modeling activities
- Design and development of construction management software
If your construction clients develop a proposed methodology, plan or design, they often don’t know if will be successful (even when using CAD modeling), until they put it into place in the construction stage. Then they must do onsite testing to ensure it passes the required benchmarks. There could be some flow into the construction stages from a qualification standpoint. But generally, when they get to the development-of-estimate phase, they’re doing initial feasibility planning and generally coming up with multiple hypotheses or methods in which they can design a building or component of a building. This is typically a good starting point for R&D activities.
LEED or green initiatives, for instance, are big qualifiers for R&D tax credits. We’re also seeing a lot of modular design or spatial design to optimize the use of space in a building tend to have good qualification potential. Typically, with construction, it’s about how we can design more efficiently in a faster, more reliable manner.
Clients often ask us: “We’re designing an entire building. How do we differentiate our time on the project between qualifying and non-qualifying?”
Typically, we rely on accounting data or time data to understand the level of tracking we have (based on employee, project and activities). We understand the project may qualify and the employee may have qualifying time. If the time is broken down into an activity basis, we can look to see if that specific activity qualifies when we look back on the construction stages. Does that activity take place at a stage that typically qualifies? If those benchmarks are passed, then we get a reasonable percentage of time applied toward that employee’s wage. We call that a PAD (Project Accounting Data) analysis. PAD helps us get a reasonable amount of time related to qualifying projects.
Real World Example
A full-service construction client of ours ($115 million in revenue) averaged over $5 million in qualified expenditures annually.
Their main activities were new building design, LEED development, electrical and plumbing systems. Their annual credit was about $450,000. The PAD analysis told us what they were working on and who was working on it. In A&E, you also have to look at fee types, since the type of fee heavily influences whether or not a project qualifies. A time and material fee is considered no-risk since you can continue to do the work without the risk of losing money no matter how long it takes. But fixed fee, by contrast, means you’re under pressure to stay on time and under budget, and stay within the design which means higher risk and potentially not being able to qualify.
Architecture
- Development of schematic design, design development, and final construction documents
- Design modification to overcome conflicts when coordinating drawings from multiple trades
- Design of unique buildings and structures
- Development of unique/custom structural support solutions
- Evaluation of multiple design solutions for technical problems
- Involving structural Integrity and custom architectural design elements
- Design activities Including estimating and programming
- Design review and modification for cost reduction and energy efficiency
- Evaluation of alternative materials for unique design requirements (e.g. sound absorption, energy efficiency, etc.)
- Development of architectural master plans
- Development of curtain wall, facade, and other building envelop systems
Typical Examples of Qualifying A&E Activities:
If you have a project that’s going to take a vast amount of design and there are uncertainties about ability, methodology and materials to be used, you will have a lot of different opportunities for R&D applicability. However, if you don’t have uncertainties, because you use the same design over and over, for instance, then there won’t be R&D qualifying activities.
If you have good project time accounting data, it really helps. You can test the projects and then figure out what your qualifying expenditures are.
Impact of recently signed Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) on Commercial and Residential Tax Incentives
Engineering
- Foundation design based on geotechnical findings
- Development of design alternatives to overcome project site issues
- Structural designs for seismic retrofits
- Development of industrial processes for production facilities
- Environmental remediation activities
- Performing CAD & BIM modeling to develop 30 building plans
- Computer modeling and simulation of design and site conditions
- Utilization of AutoCAD, REVIT, BIM, HEC·RAS, STAAD, and ANSYS
- Design changes and modifications due to regulatory compliance issues
1. Commercial
EPAct §179D, is a tax deduction for commercial building owners, and design firms that have built, installed, or retrofitted their properties to be more energy efficient. They can deduct all or part of the costs associated with the construction, installation or retrofit in the amount of up to $1.88 per square foot.
The three main components needed to qualify for §179D are:
- The interior lighting system.
- The HVAC and domestic hot water system.
- The building envelope (roof, walls, window systems).
Now that the IRA has passed, starting in 2023 the deduction increases to between $2.50/sf and $5.00/sf for 25% to 50% energy savings that meet new prevailing wage and apprenticeship requirements. If those conditions ARE NOT met, the deduction is reduced to $2.50/sf and $5.00/sf.
In the past, government projects were the only ones that could allocate the deduction to the architecture and engineering firms. Starting in 2023, the designer allocation will be open to all tax-exempt entities including Indian tribal governments, private colleges and universities.
If you have retrofit projects, until year-end 2022, you can still compare your proposed building to an ASHRAE 90.1 building and qualify those projects. Starting in 2023, however, you have an alternative tax deduction. The proposed building and its energy efficiency measures (i.e., lighting, HVAC, building envelope) must be compared to the existing building’s energy use intensity. You’re talking about collecting 12 months of utility data prior to construction starting, to establish your baseline. Then 12 months after the construction is completed you look at your new utility data and compare it to your utility data before construction began. Based on the post-construction savings you achieve; your tax deduction amounts to between $0.50 to $5.00 per square foot.
For existing buildings going through renovations, the key is to have a retrofit plan in place BEFORE construction starts. The retrofit plan must be signed by a registered architect or professional engineer and verifying that at minimum, there will be 25% savings compared to the existing building.
2. Residential
IRC §45L New Energy Efficient Home Credit is for developers of energy-efficient dwelling units, including single-family homes, multifamily buildings, and even mobile homes. The IRA extends the current §45L credit for dwelling units acquired by sale or lease for use as a residence through December 31, 2022. For units acquired starting on January 1, 2023, there are substantial changes to the credit rate and qualifications:
For single family homes:
- Projects must meet the “ENERGY STAR” qualification in order to get the tax break. Energy Star is the government-backed symbol for energy efficiency.
- If the new standard is met, the tax credit increases to $2,500 per unit from the current $2,000.
- If you meet the Zero Energy Ready Home (ZERH) standard, the credit goes up to $5,000 per unit.
- In either case there is no prevailing wage requirement.
For multi-family homes:
- Projects must also meet the ENERGY STAR standard to get the tax break.
- The credit increases to $2,500 for meeting ENERGY STAR certification or to $5,000 if meeting the ZERH program (assuming prevailing wage requirements are met).
- If prevailing wage requirements are not met, the credit is reduced to $500 for ENERGY STAR certification and to $1,000 for the ZERH program.
TCJA Changes That Could Impact R&D
For A&E and construction firms, changes stemming from the 2017 Tax Cuts & Jobs Act (TCJA) could make the economics of the R&D credit more difficult to justify. No one knows for sure if these long-delayed changes will be enacted until after the mid-term election dust settles, but it pays to be prepared. TCJA said that in addition to requiring research expenditures to be amortized, all software development will now be considered an R&E expenditure. The research credit itself is not directly affected, but it does affect the economics of research in three primary ways:
- You’re no longer looking at expense; you’re primarily looking at capitalized and amortized costs.
- The §280C election allows you to take a reduced credit. If taxpayers DO NOT elect the reduced credit under §280C, the excess of the research credit over the current year R&E amortization deduction reduces the current year amount of R&E capitalized. For instance, in 2022, the research credit percentage will need to exceed 10% for a taxpayer to experience any addback. Electing the reduced credit will no longer be advantageous for many taxpayers.
- The reasonableness requirement under § 174 is eliminated. That’s good news for research-oriented firms.
Compliance Issues
§45L issues + cost seg
For residential dwellings, be careful about taking the §45L energy efficiency credit if you’re also doing a cost segregation study on the property. Ordering matters! If you’ve already taken the credit, that’s no longer a 3115. You must pay the $11,500 IRS user fee and file by the end of the year in order to make a method change. It’s a lot of added expense. If you have the option, file the 3115, wait for it to be effective, then file the amended returns.
§179D
For Building Owners
- 179D is available on timely filed, original returns subject to normal 9100 late election relief.
- 179D elections can be made on automatic Form 3115, including for closed tax years.
- Bonus depreciation (QIP) or 179 expensing (QRP) may eliminate federal benefit
For Designers
- 179D is available on timely filed, original returns.
- 179D is also available on amended returns for open tax years.
- No Form 3115 late election relief available.
Conclusion
If your clients or organization would like amore guidance and resources about how claiming the maximum benefits of these and other credits and provisions, please don’t hesitate to contact us.





